Introduction
Italy is a fascinating country for population geneticists and historians alike. As Metternich said in 1847 "Italy is only a geographical expression". The peninsula was unified by Piedmont two decades later, but Metternich's remark still largely holds true today. There isn't one Italian people, but a multitude of ethnic and cultural groups, often with an independent history of their own going back to ancient times.
Countless people have settled in Italy since the Neolithic: Near Eastern farmers, Italic tribes, Ligurians, Etruscans, Phoenicians, Greeks, Celts, Goths, Lombards, Byzantines, Franks, Normans, Swabians, Arabs, Berbers, Albanians, Austrians and more. All have left their genetic print on the populations of the regions where they settled. This page attempts to identify their genetic markers through the use of Y-chromosomal haplogroups, which are passed on nearly unaltered from father to son.
History of the peoples and tribes who made Italy
| If you are new to population genetics... |
|---|
|
In the following section we will review the Y-DNA haplogroups of the various prehistoric and historical populations that have settled in Italy since Cro-Magnon colonised Europe during the Ice Age. that If you are unfamiliar with haplogroups or population genetics, we recommend that you familiarise yourself first with the basics by viewing the Video Tutorials about genetics and read our Frequently Asked Questions about DNA tests. Each haplogroup corresponds to a distinct ancestral lineage. Haplogroups are divided into numerous levels of subclades that form a phylogenetic tree, which is just a fancy word for genealogical tree of genetic ancestry. You may also find it useful to visualise the modern distribution of Y-DNA haplogroups to get a sense of they represent. Detailed descriptions of each haplogroup and their history are available here, but links to each haplogroup's page are also provided in the text below.
|
Paleolithic to Neolithic
Europe has been inhabited by modern humans for over 40,000 years. Three thirds of this time corresponds to the Ice Age, a period when humans lived as nomadic hunter-gatherers in small tribes. During the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), which lasted approximately from 26,500 to 19,000 years ago, most of northern and central Europe was covered by ice sheets and was virtually uninhabitable for humans. Italy was one of the temperate refugia for Cro-Magnons. It is thought that Cro-Magnons belonged chiefly to Y-DNA haplogroups F and I.
There are few surviving paternal lineages of Cro-Magnons in modern Italy. Pockets of haplogroup I2* and I2c (L596) have been observed at very low frequency in Northwest Italy, between the Alps and Tuscany. It is not certain, however, that these lineages remained in Italy since the Ice Age. They could have come from other parts of Europe later on, notably with the Celts, who also brought I2a2b (L38). Germanic tribes are brought haplogroup I1 and I2a2a (M223). Some or all of these lineages might be descended from Cro-Magnons from the Italian peninsula who migrated north when the climate warmed up 10,000 years ago.
The most common variey of haplogroup I in Italy is I2a1a (M26), which is found mostly in Sardinia (36% of the male lineages) and to a lower extent in Iberia and coastal areas of the Western Mediterranean. It is still unclear where I2a1 (P214) developed. It could have been in Italy, in the Balkans, or even further east in the Carpathians and north of the Black Sea. According to current estimates, I2a1 appeared about 20,000 years ago, close to the end of the LGM, and split almost immediately into western branch (M26) and an eastern one (M423). In all likelihood, the territory of the nomadic I2a1 people must have included Northeast Italy and the Dinaric Alps within the refugium. The tribe grew and split, with some branches going west to Italy and the Western Mediterranean, and the other going east to the Balkans and the Pontic Steppe.
By the time the first Neolithic farmers and herders arrived in Italy from the Near East 8,000 years ago most of the peninsula could well have been inhabited by I2a1a hunter-gatherers. Agriculture had appeared in the Levant at least 11,500 years ago. In the ensuing two and a half millennia it spread slowly to Anatolia and Greece. From Greece, it took another millennium for Neolithic farmers to cross the sea to Apulia, Calabria, Sicily and Sardinia, and from there move inland and colonised the rest of the peninsula for yet another millennium. Around 7,000 years ago all Italy bar the remotest corners of the Alps had adopted agriculture. The Near-Eastern newcomers belonged essentially to haplogroup G2a, and seem to have carried a minority of E1b1b, J*, J1, J2 and T lineages. The majority of modern Italian E1b1b and J2 came later though, with the Etruscans, the Greeks, and the various Near Eastern people who settled in Italy during the Roman Empire, particularly the Jews and the Syrians.
Hunter-gatherers appear yo have mostly fled the peninsula after the arrival of Neolithic farmers, except in Sardinia, where they blended with them, perhaps trapped by the sea and unable to do otherwise. Nowadays, Sardinians are the population resembling most closely Neolithic Europeans. This was already known from archeological and anthropoligical studies, but was confirmed by the testing of ÷tzi's genome, a 5,300 year-old man mummified in the ice of the Italian Alps, and whose DNA was found to be very close to that of modern Sardinians. The geographic isolation of Sardinia has left its inhabitants to a large degree unaffected by outside influences, apart from a minority of Phoenician, Roman and Vandal colonisers. For example, the combined 3% of hapogroups I1, I2a2a and R1a could be attributed to the Vandals, a Germanic tribe who ruled over Sardinia from 435 to 534. The Romans left some 10% of R1b-U152, and probably some additional E1b1b, G2a and J2 lineages.
Bronze Age to Iron Age
Italics & Romans
The Bronze Age was brought to Europe by the Proto-Indo-Europeans, who migrated from the North Caucasus and the Pontic Steppe to the Balkans (from circa 6,000 years ago), then went up the Danube and invaded Central and Western Europe (from 4,500 years ago). Italic-speakers, an Indo-European branch, are thought to have crossed the Alps and invaded the Italian peninsula around 3,200 years ago, establishing the Villanova culture and bringing with them primarily R1b-U152 lineages and replacing or displacing a large part of the indigenous people. The Neolithic inhabitants of Italy sought refuge in the Apeninne mountains and in Sardinia. Nowadays, the highest concentration of haplogroup G2a and J1 outside the Middle East are found in the Apeninnes, Calabria, Sicily and Sardinia.
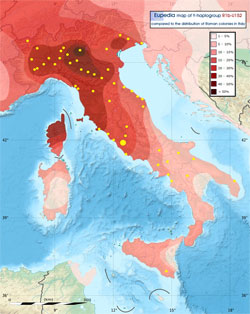
Italic tribes conquered the whole peninsula, but settled most heavily in northern and central-west Italy, especially in the Po Valley and Tuscany, but also in Umbria and the Latium, who both owe their names to Italic tribes (the Umbrians and the Latins). In all logic, the ancient Romans, from the original founders of Rome to the patricians of the Roman Republic, should have been essentially R1b-U152 people, with a minority of G2a-L140 (L13, L1264 and Z1816 subclades) and J2a1-L70 (PF5456 and Z2177 subclades). Those G2a and J2a1 lineages would have been assimilated either in the Steppe or in Southeast Europe before the Proto-Italics reached the Alps. Based on modern frequencies in northern and central Italy, each would have been 5 to 10x less common than R1b-U152. Intermarriages with their Etruscan and Greek neighbours would have gradually brought other paternal lineages to the Roman gene pool, including other G2a and J2 subclades, but also haplogroups such as E1b1b and T1a (see below).
An additional clue that the inhabitants of the Roman Republic still belonged predominantly to R1b-U152 comes from the modern population in the cities they founded. It is remarkable that most of the cities founded during the Roman Republic by Roman colonists in northern Italy (Alba, Aosta, Asti, Bologna, Brescia, Casale Monferrato, Cremona, Ferrara, Forlž, Ivrea, Lodi, Massa, Milan, Modena, Monza, Parma, Pavia, Piacenza, Pistoia, Pollenzo, Reggio Emilia, Rimini, Sarzana, Torino, Tortona) are located in the areas with the highest incidence of R1b-U152 (and lowest incidence of E1b1b and J2) today. Only a handful of Roman colonies were set up in north-east Italy (Aquileia, Belluno, Pordenone, Vicenza), four in the Marches (Ancona, Macerata, Pesaro and Senigallia), and not a single one in the modern region of Liguria.
Naturally U152 was already present in northern Italy before the Roman period. But if the Roman colonists had not been predominantly U152, its frequency would have been diluted by the newcomers. What we observe is the reverse; the frequency of U152 has been amplified around Roman colonies.
R1b-U152 has also been found a low frequencies (1 to 10%) almost everywhere within the boundaries of the Roman Empire, even in regions where no other R1b-U152 people (e.g. Hallstatt/La TŤne Celts) ever settled, such as Sardinia and North Africa. On the other hand, not all U152 in southern Italy may be of Italic or direct Roman origin. Some of it may be attributed to the Normans (those of Gallo-Roman rather than Viking descent) and Swabian Germans during the Middle Ages, especially in Sicily. It is still difficult at present to differentiate the Celtic vs Italic origin of the various U152 subclades. Z56 appears to be the most Italic or Roman subclade, and particularly its Z72 clade. It is rare outside Italy and has a distribution focused on central Italy. Nevertheless other branches may also be Italic, including a few L2 subclades.
During the Late Bronze Age and in the Early Iron Age other Indo-European tribes also settled in northern Italy, like the Ligures in Liguria, the Lepontic and Gaulish Celts in Piedmont, and the Adriatic Veneti in Veneto.
According to the founding myth of Rome, Romulus and Remus descended from the Latin kings of Alba Longa, themselves descended from Trojan prince Aeneas, who fled to the Latium after the destruction of Troy by the Greeks. Troy may well have been founded by the early M269 and/or L23 branches of R1b, representing the first expansion of R1b from the Pontic Steppe to the Balkans (see R1b history). If there is any truth in the myth (as there usually is), the Trojans might have brought M269 or L23 (probably with other haplogroups, notably J2) to central Italy circa 1200 BCE, around the same time as U152 invaded from the north. The Etruscans, who are thought to have originated in western Anatolia, not far from Troy, might also have brought R1b-L23 to Italy, also blended with other haplogroups (see below). Nowadays R1b-L23 is the second most common subclade of R1b in Italy (see map), although well behind R1b-U152. L23 has a remarkably uniform distribution over all the Italian peninsula, making between 5% and 10% of the male lineages. It is found at a slightly higher frequency in Campania and Calabria due to the Greek colonies, and decreases under 5% of the population only around the Alps.
The study of Sardinian Y-DNA by Francalacci et al. (2013) allowed to have a look at the subclades of R1b on this island that has not been settled by the Celts or the Etruscans, nor by an Italic tribe besides the Romans. The Greeks only had a brief a foothold at Olbia and would not have influence the genetics of the island. In other words, all the Indo-European R1b in Sardinia (bar a tiny percentage of Germanic R1b brought by the Vandals) can be attributed to the Romans. The results are unequivocal, R1b-U152 makes up 10.5% of all Sardinian lineages, while R1b-M269 and R1b-L23 together amount to a mere 1.5%. This is yet more evidence that U152 was probably the dominant Roman lineages. The Sardinian U152 samples can be used to distinguish Roman subclades of U152 from other Italic and Alpine Celtic subclades. All four top level subclades of U152 were found in Sardinia, but in very different proportions from the continent, especially north of the Alps where L2 makes up over two thirds of the lineages. In contrast, Z192 is the main subclade in Sardinia (58.5% of all U152), followed by Z56 (10%, half of being Z144+), L2 (7.8%, exclusively Z49+ and Z347+) and Z36 (5.5%, half of it Z54+).
The analysis of Sardinian lineages hint that the ancient Latins/Romans did not carry a lot of E1b1b lineages, if any. Out of 9.5% of E1b1b in Sardinia, some 6% belongs to the North African M81 subclade, almost certainly dating from the time when Sardinia was a Phoenician/Carthaginian colony with intensive links with North Africa. The remaining 3.5% ought to be mostly of Neolithic and Phoenician origin (see details), meaning that the Romans probably didn't bring E1b1b lineages. The percentage of haplogroup J2 in Sardinia that could be Roman is comprised between 2% and 6%, so probably less than half, and perhaps as little as a fifth of the percentage of R1b-U152. Haplogroup G2a in Sardinia is widely believed to be chiefly of Neolithic origin, although a few percents could be Phoenician or Roman. The Roman form of G2a is almost certainly G2a3b1a and its two main subclades U1 and L497, whose distribution in Europe mirrors that of R1b-U152. These subclades make up 1.5% of Sardinian lineages, a proportion of 1/7 compared to R1b-U152.
Etruscans, Phoenicians & Greeks
Between 1200 and 539 BCE the Phoenicians built a vast commercial empire from their Levantine homeland along the southern Mediterranean as far as Iberia. In Italy they had colonies in western Sicily and southern and western Sardinia. Based on the haplogroups found in modern Lebanon and in their former colonies, the Phoenicians seem to have carried a mixture of haplogroup J2, J1, E1b1b, G, R1b-M269/L23, T, L, R1b-V88, R2 and Q, roughly in that order of frequency. By comparing Sardinian and Lebanese DNA, it can be estimated that the Sardinians have inherited between 16% and 24% of their Y-DNA from the Phoenicians (see details).
The autosomal data provided by Haak et al 2015 (extended data figure) shows that the Sardinians only differ from the Basques by the presence of Bedouin-like (purple) and Caucaso-Gedrosian (greyish green) admixture, and a slightly more elevated percentage of Neolithic farmer ancestry (orange). These three components are found in roughly equal proportion in the modern Lebanese, and lumped together would account for 10 to 15% of the Sardinian DNA. This is the best estimate at present of the genome-wide contributions of the Phoenicians to the modern Sardinian population. It is not surprising that the presumed percentage of Phoenician Y-DNA should be a bit higher, as men typically made up a larger proportion of colonists in ancient times.
Another key player in the make-up of Iron Age Italy were the Etruscans, who appeared circa 750 BCE apparently out of nowhere. Some have postulated that they came from Anatolia, but their origins remain uncertain to this day. Although their territory matches closely the extent of the Italic haplogroup R1b-U152, the Etruscans were non-Indo-European speakers, and their language is unrelated to any other known ancient languages apart from the Raetic language of the Alps and the Lemnian language of the Aegean Sea. It is likely that the Etruscans came from somewhere in the Eastern Mediterranean and imposed their language on the Italic tribes living in Tuscany, then to the Po Valley, thus splitting Indo-European-speaking tribes in two. Based on the non-Indo-European halogroups found in central and southern Tuscany today, the original Etruscans probably belonged to an compound of haplogroups J2, E1b1b, G2a, and R1b-M269 (or R1b-L23) in that order of frequency. This would appear to support of Greek or West Anatolian origin. The high frequency of R1b-U152 found in Tuscany today can be attributed to Italic tribes absorbed by the Etruscans, and to the Romans who resettled part of Etruria.
It is the ancient Greeks who had the biggest impact on the genetic make-up of southern Italy. From the 8th century BCE the Greeks set up colonies all along the coasts of Campania, Calabria, Basilicata, southern Apulia, and Sicily (except the western tip) in what would become known as Magna Graecia. Their genetic signature are essentially haplogroups J2 (18-30%) and E1b1b (15-25%), but the ancient Greeks also carried some R1b-M269/L23 (5-10%), G2a (3-8%), T (1-6%), I2a1b (1-5%), R1a (1-3%), and J1 (1-2%). It is very clear on the haplogroup maps that the areas in central and southern Italy furthest from the coast and from ancient Greek colonies, such as Abruzzo, Molise and the southern Apennines correspond to the highest percentages of haplogroups G2a, J1 and T in Italy, but also the lowest frequency of E1b1b and J2 in the southern half of Italy. There is no better way to contrast the Neolithic population of Italy with the ancient Greek colonists.
The Greeks also colonised Liguria and the French Riviera, where they founded Genoa, Nice (which was an Italian city until 1860) and Marseille. The Phoenicians and Cartaginians also kept bases in Liguria at some point. Modern Ligurians have the highest percentage of haplogroup E1b1b outside southern Italy (almost entirely the Greek E-V13), but also the highest level of G2a and J1 outside the Apennines, which probably means that this mountainous region also served as a shelter to Neolithic populations during the Italic invasions. R1b makes up about half of Ligurian lineages, among which 22% belong to the U152 subclade, 20% to P312 (the highest level in Italy), 6% to L23, and 2% to L21. The ancient Ligures spoke a language intermediary between Celtic (P312, L21) and Italic (U152) families, and their Y-DNA is split exactly in half between Italic and Celtic. The 6% of L23 are probably of Greek origin. Overall about one third of the modern Ligurian lineages could be of Greek origin.
Roman Empire & Middle Ages
In the first century Rome became the capital of a vast, cosmopolitan empire. Immigration to Rome made the city grow from a population of approximately 400,000 in the third century BCE, before Rome started expanding outside the Italian peninsula, to at least 1 million under the reign of Emperor Augustus (27 BCE to 14 CE). As those migrants came from every part of the empire it is very hard to estimate how much impact they had on the demographics of Rome and the Italian peninsula, but it was surely considerable in the Latium region.
Goths, Lombards & Byzantines
In the 4th and 5th centuries the cooling of the climate prompted Germanic and Slavic tribes to migrate south and west and to invade the Roman Empire in search of more fertile lands. Germanic people brought haplogroups I1, I2a2a (M223, formerly known as I2b1), R1b-U106 and R1a (L664, Z282 and Z283 subclades) to Italy.
The Vandals were the first to reach the Italian peninsula. They had migrated to Iberia, then crossed over the North Africa in 429, where they founded a kingdom that also comprised Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica. Sardinia is the best place to look for traces of their DNA because on the one hand it is the best studied region of Italy, and on the other hand no other Germanic peoples settled there (apart from a very brief Gothic reign), which means that the presence of Germanic lineages on the island would incontestably be of Vandalic origin. Based on the detailed Y-chromosomal study of 1200 Sardinians by Francalacci et al. (2013), the Vandals appeared to have carried 35% of R1a, 29% of I2a2a, 24% of R1b, 6% of I2a1b and a mere 6% of I1. The subclades identified were I1a3a2 (L1237+), I2a2a (L699+ and CTS616+), I2a1b (M423+), R1a-Z282 (incl. some Z280+), R1a-M458 (L1029+), R1b-U106 (Z381+), R1b-L21 (DF13>L513+), R1b-DF27 (Z196>Z209+). The probable the reason for the elevated (Proto-)Slavic R1a and the presence of the Eastern European I2-M423 is that the Vandals stayed in Poland before migrating to the Roman Empire. Over a third of Vandalic male lineages were therefore of Proto-Slavic origin.
In 475, various East Germanic tribes (Herulians, Rugians, and Scirians) were refused federated status by Roman emperor. Under the leadership of Odoacer, a former secretary of Attila, they deposed the last emperor and created the first Kingdom of Italy (476-493), bringing to an end the Western Roman Empire. The kingdom was taken over by the Ostrogoths, who ruled the whole of Italy except Sardinia until 553. The Ostrogoths's capital was Ravenna. They were succeeded by the Lombards (568-774), who had to contend for the political control of Italy with the Byzantines. Like the Ostrogoths, the Lombards had invaded Italy from Pannonia and settled more densely in north-east Italy and in Lombardy, which was named after them. The Lombard capital was in Pavia, Lombardy. They set up many duchies, notably those of Friuli (based in Cividale), Trento, Tuscany (based in Lucca), Spoleto, Benevento, as well as in the major cities of Lombardy and Venetia.
The genes of the Goths and the Lombards became quickly diluted into the Italian population owing to their relatively small number and their geographic dispersal in order to rule and administer their kingdom. Both the Goths and the Lombards originated in southern Sweden. Their migration path differed considerably though. The Goths descended through modern Poland as far as the Black Sea, where they surely intermingled with the local populations, then moved into the Balkans in the middle of the 3rd century, where they remained until the 5th century. Considering the high percentage of R1a identified in Vandalic settlements in Sardinia, it wouldn't be unreasonable to think that the over half of the Gothic lineages had become Proto-Slavic (R1a and I2a1b) by the time they reached the Balkans. It was common practice at the time for Eastern European tribes to converge and retain the name of the dominant tribe. Around the same period the Huns had also been a compound of several ethnicities brought together under Hunnic leadership. The Goths would have subsequently blended to some extent with the native inhabitants of the Balkans in the two centuries preceding their invasion of Italy, assimilating mostly J2, E1b1b and more I2a1b lineages. In the 5th century the Goths would have become such a melting pot that their original Germanic Y-DNA might have only represented a small percentage of their lineages. This explains why there is apparently so little Germanic Y-DNA in south-western France and Spain (location of the former Visigothic kingdom) compared to other regions conquered by Germanic tribes in Western Europe, including Italy.
In contrast with the Goths and the Vandals, the Lombards left Scandinavia and descended due south through Germany, Austria and Slovenia, only leaving Germanic territory a few decades before reaching Italy. The Lombards would have consequently remained a predominantly Germanic tribe by the time they invaded Italy.The DNA samples from Campobasso in Molise and Benevento in Campania can give a good idea of what proportion of each Germanic haplogroup the Lombards carried. Campobasso was founded by the Lombards are lost its importance after Lombard rule. Benevento was the seat of a powerful Lombard duchy. Among the Germanic haplogroups identified in Campobasso by Boattini et al. (2013) there were 16% of I1, 10.5% of R1b-U106 and 3.5% of I2a2a. No R1a was found. The same study reported 5.5% of R1a, 2.5% of I1, and 2.5% of R1b-U106 in Benevento. If we make the average, the Lombards seem to have had roughly 40% of I1, 30% of R1b, 25% of R1a and 5% of I2a2a, a frequency comparable to that of modern Sweden.
Some regions were never under Lombard domination, including Sardinia, Sicily, Calabria, southern Apulia, Naples and the Latium. In all these regions the Byzantines brought more Greco-Anatolian lineages (especially E1b1b and J2), which were already the dominant lineages from the Magna Graecia period. The Byzantines may have changed slightly the balance of haplogroups in southern Italy, but their impact might have been more contrasting in the parts of northern Italy that belonged to the Exarchate of Ravenna, namely Romagna, Marche, coastal Veneto and Liguria. It may be a coincidence, but these regions happen to be exactly the ones where haplogroups J2 and E1b1b reach frequencies comparable to Greece and western Anatolia. J2 was not a major Neolithic lineage, and the Greeks did not colonise northern Italy (apart from Liguria) in ancient times. The Etruscans could have spread E1b1b and J2 to Emilia-Romagna, but were not present in the other regions. The establishment of a Byzantine population is therefore the best explanation for the high frequency of E1b1b and J2 in Veneto and the Marches. The region of Constantinople has one of the highest percentage of haplogroup J2 anywhere.
Franks, Arabs & Normans
The Franks conquered the Lombard kingdom of Italy in 774. Contrarily to other Germanic tribes before them, the aim of the Franks was not to find a new homeland. Consequently, they did not migrate en masse to Italy. They only brought soldiers and administrators (not necessarily of Frankish descent, but also former Gallo-Romans), like the Romans had done when they expanded their empire. Their genetic print is therefore more elusive, although they surely increased a bit the proportion of I1 and R1b-U106.
Soon after the arrival of the Franks, the Saracens invaded Sicily, where they established an emirate (831-1072). Most Muslims left after the Normans reconquered the island in the 11th century. Sicily has nevertheless slightly higher percentages of Southwest Asian haplogroup J1 and North African haplogroup E-M81 than the rest of southern Italy. The Arabs are known to have spread the J1 lineage during the spread of Islam. However the Phoenician colonies in Sicily could just as well be the cause of the higher J1 in Sicily. Likewise, E-M81 is the Berber haplogroup, but its presence in Sicily could date back to Phoenician, Roman or Vandal times, when exchanges were frequent between Sicily and Tunisia.
The Normans left a much clearer print on Sicily and southern Italy. Originally Vikings from Denmark, the Normans were granted a duchy by the King of France in 911. From 999, invited by the Prince of Salerno, Norman knights started serving as mercenaries for the Lombards against the Byzantines. They quickly acquired counties and duchies of their own and set about to unify all southern Italy under their rule. In 1061 they invaded Sicily, which was completely conquered in 1091. The Norman Kingdom of Sicily was created in 1130, with Palermo as capital, and would last until the 19th century. Nowadays it is in north-west Sicily, around Palermo and Trapani, that Norman Y-DNA is the most common, with 8 to 15% of the lineages belonging to haplogroup I1.
Distribution maps of Y-DNA haplogroups in Italy
Y-DNA frequencies by region
Total samples for Italy = 6145.
For the regions, the first row shows the number of samples, while the second row is the percentage for each haplogroup.